An uninterruptible power supply, also uninterruptible power source, UPS or battery/flywheel backup, is an electrical apparatus that provides emergency power to a load when the input power source or main power fails. A UPS differs from an auxiliary or emergency power system or standby generator in that it will provide near-instantaneous protection from input power interruptions, by supplying energy stored in batteries,supercapacitors, or flywheels. The on-battery runtime of most uninterruptible power sources is relatively short (only a few minutes) but sufficient to start a standby power source or properly shut down the protected equipment.
A UPS is typically used to protect hardware such as computers,data centers,telecommuincation equipment or other electrical equipment where an unexpected power disruption could cause injuries, fatalities, serious business disruption or data loss. UPS units range in size from units designed to protect a single computer without a video monitor (around 200 volt-ampere rating) to large units powering entire data centers or buildings. The world's largest UPS, the 46-megawatt Battery Electric Storage System (BESS), in Fairbanks,Alaska, powers the entire city and nearby rural communities during outages.
In general, a UPS protects IT equipment and other electrical loads from problems t hat plague our electrical supply.
1.It prevents hardware damage typically caused by surges and spikes. Many UPS models continually condition
incoming power as well
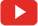
In electrical engineering, single-phase electric power refers to the distribution of alternating current electric
power using a system in which all the voltages of the supply vary in unison. Single-phase distribution is
used when loads are mostly lighting and heating, with few small electric motors.
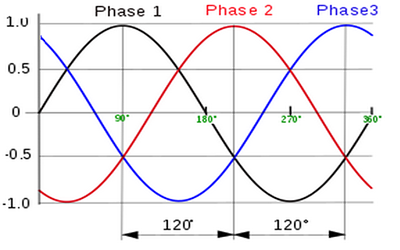
As well being the most efficient way to distribute power over long distances, three-phase power also enables
industrial equipment to operate more efficiently. Three-phase power is characterised by three single-phase
waves that are offset in their phase angle by 120 degrees, or one third of the sine wave period.
4. Which one best fits your customers’needs?
The different UPS topologies provide varying degrees of protection. There are several factors that determine
which one will best fit your customers’ needs, including the level of reliability and availability they
require, the type of equipment being protected and the application or environment in question.
5. UPS form factors
Because UPS are used for many different applications - ranging from desktop systems to large data
center ,they come in a wide variety of form factors.
4.Large Tower UPS
6. UPS battery overview
It’s a well-known fact that the battery is the most vulnerable part of a UPS. In fact, battery failure
is a leading cause of load loss. Understanding how to properly maintain and manage UPS
batteries can not only extend battery service life, but can also help prevent costly
downtime.
7. Factors affecting battery life
All UPS batteries have a limited service life, regardless of how or where the UPS is deployed.
While determining battery life can be tricky, there are four primary factors that affect a
battery’s overall lifespan.
8. Worldwide voltage map
1. Why A UPS ?

2. Single Phase Power
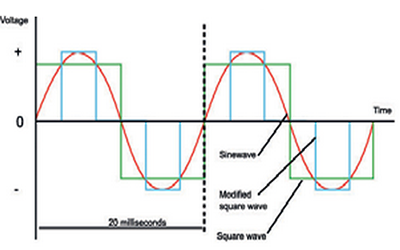
3. Three Phase Power


2.Rack mount UPS
3.Scalable UPS


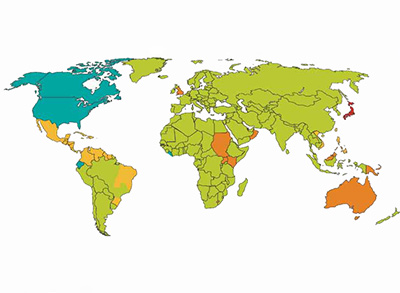
In the world, different countries have different requirements for AC voltage and frequency.
For exmaple
In China Single phase voltage : 220VAC Three phase Voltage : 380VAC Frequency : 50HZ
In UK Single phase voltage : 240VAC Three phase Voltage : 415VAC Frequency : 50HZ
In Mexico Single phase voltage : 127VAC Three phase Voltage : 220/480VAC Frequency : 60HZ
 global
global